Over 150 years ago, someone had the bright idea of creating a light bulb, a lighting solution that could be used in our homes and offices. However, the question of who invented the light bulb remains confusing to this day.
All we know for sure is that, because of this invention, hardly a day passes today without you seeing the light bulb. It's one of the first things you see after getting up. You could even say that bulbs literally brighten your day.
Before the idea of a light bulb came about, people used open flames and gas as light sources. Therefore, the introduction of a light bulb was a welcoming change.
But the big question is: who invented the light bulb? Many people think Thomas Edison did, but that's actually not the case, although the famed engineer played a considerable role in creating the light bulb as we know it today.
Edison had 1,000 patents, and one of them involved a light bulb. The patent, however, was about the improvements he made on this important invention.
Sadly, most people completely forgot about the scientists who invented the light bulb due to Edison's towering influence on its history. That is why many people mistakenly assume he made this important invention.
Edison worked on creating a more efficient, practical, and affordable product. In fact, he bought patents from the people who invented the light bulb before making the best of this invention.
Due to this, the question of who invented the light bulb has not always been easy to answer.
So, Who Invented The Light Bulb?
In 1800, Alessandro Volta, an Italian inventor, created one of the first devices used to produce electricity. He invented the "voltaic pile," a crude battery made using zinc, copper, cardboard, and saltwater. The term "volt" was derived from Volta's name.
But no, Volta is not the man who invented the light bulb.
It was only in 1806, a couple of years later, that Humphry Davy came up with the electric arc lamp, and it relied on a battery similar to the one invented by Volta. The arc lamps had electrodes that ionized gas to produce light.
The major downside of this battery was the excess brightness and short operation time. The light was too bright to be used in homes. For this reason, the arc lamp was not exactly a roaring success.
Nonetheless, that makes Davy one of the people who invented the light bulb, although his version required a lot of important modifications before becoming a mainstream product.
In any case, experiments with compounds that could produce light when heated up, a process known as incandescence, also started around this time. However, some materials heated up so much that they burned up and melted.
Eventually, researchers discovered a filament, which could last a lot longer. This discovery turned out to be a real game-changer. It was also discovered that enclosing the filament in a vacuum kept it working for extended periods of time.
In 1840, Warren de la Rue found out that using a platinum filament made the bulb last longer than a copper filament would. He chose the material because of its high melting point. He also put the filament in a vacuum space as the reduced exposure to air reduced the chances of it reacting with the air and burning out.
However, once again, there was a problem. Platinum was too expensive for commercial use, and vacuums were not that easy to create at the time. The bulbs also required a lot of electricity to glow. Despite all this, de la Rue deserves a lot of credit for being one of the men who invented the light bulb.
The arc lamp was improved in 1848 when William Staite added a clockwork mechanism that dictated how the carbon rods moved. Unfortunately, this light required expensive batteries which made it less successful commercially.
Who Invented The Light Bulb We Use Today?

From early on, it was clear that making a cost-effective lighting solution was the way to go, and that is why the man who made this happen, Thomas Edison, is often considered the person who invented the light bulb.
However, just like Edison, Joseph Swan, a British physicist, worked on this problem in the mid-1800s.
To keep the cost of the filaments down, Swan tried using carbonized paper. Unfortunately, it burned out too quickly. His attempts to use cotton threads had the same challenge and proved impractical.
Luckily, the Sprengel air pump was discovered in 1877, allowing scientists to create better vacuums. This kept the filaments burning for much longer.
Swan created a bulb that used a cotton filament covered in acid. However, after several weeks, the bulb failed because the filament was thick and needed a lot of power to glow.
Undeterred, Swan kept experimenting, but his basic design and innovations made him one of the men who invented the light bulb.
Edison's Experiments With The Light Bulb

If his claims are to be believed, Thomas Edison tried using more than 6,000 different organic materials while researching the best filament for an improved incandescent light bulb.
His extensive work on this invention has led many to believe he is the person who invented the light bulb.
However, a bulb existed before he came along. His goal was to make the bulb affordable and reliable, just like Swan was trying to do. In the end, he concluded that the correct bulb needed a thin filament that did not need a large electric current.
Edison would work for up to 20 hours per day, testing various designs. He met his first success when he created a bulb with a platinum filament. It was on for 40 minutes before it burned out.
Although he was unsuccessful, he was so confident that he was about to be victorious that he got a $300,000 loan to create the Edison Electric Light Company. J.P. Morgan was among the company's first investors.
The publicity he got from this bold step made much of the world think he was the man who invented the light bulb.
Edison Discovered That Tungsten Was Ideal For Light Bulbs

After forming his company, Edison tested more than 300 filament materials in more than 1,400 experiments. Among the things they tested were cedar, flax, and hickory.
He also tried tungsten, a material that would be pretty common in bulbs later on. However, at the time, he lacked the tools to make the best use of this material, although he believed it was the best material to use as a filament.
However, in 1879, he met with success after making a bulb using a cotton filament that burned for 14.5 hours. Edison also found that higher resistance was preferable as it made bulbs glow more easily.
For this reason, Edison has the honor of being the person who made the incandescent light bulb get its first practical use. Eventually, he made a filament using bamboo that lasted 1,200 hours, and he got a patent for it on January 27, 1880.
Since many of the first bulbs people used were created by Edison, they believed he was the person who invented the light bulb.
Even after the patent, he went on working on the light bulb. This included creating a socket screw and better vacuum pumps that helped make better quality light bulbs.
Eventually, one of the researchers associated with Edison found a patent for making a carbon filament more efficiently. Another patent was later filed for a means to make the bulb burn bright without darkening the glass bulb.
In 1892, General Electric was formed. The company had power plants and also developed power meters to determine usage. These innovations helped make incandescent lighting a critical part of society.
Consequently, electric light was being used all around the world, and Edison was seen as the person who invented the light bulb.
Edison And Swan's Work On The Light Bulb
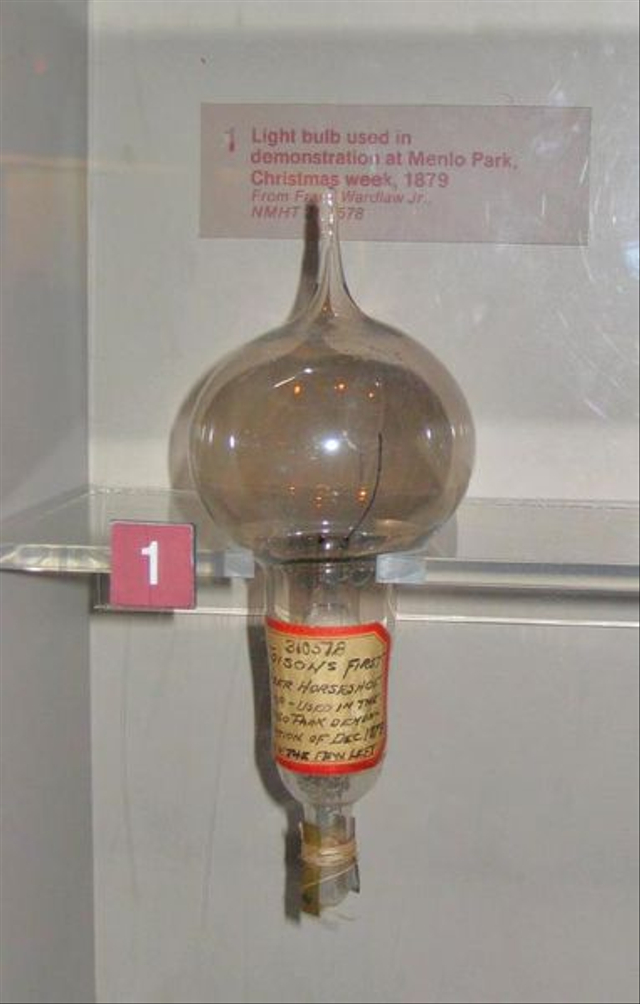

Even as Edison worked hard to create the perfect light bulb, Joseph Swan was also perfecting his bulb and got a patent on November 27, 1880. Swan's home became the first to get powered by electricity.
Swan also helped power Savoy Theater in 1881, making it the first public building to be lit by electricity. So, according to the UK, Swan was the man who invented the light bulb.
In the same year, he made these historical breakthroughs. He founded Swan United Electric Light Company. Edison sued him for copyright infringement, but the British courts ruled in Swan's favor. The truth is that the two had filed their patents at almost the same time.
However, Swan and Edison managed to work together. They founded Ediswan and provided electricity to the U.K.
The relationship forced Swan to support Edison's patents. Swan remained in his shadow, although some felt that he was the person who invented the light bulb.
He was knighted in 1904 for his achievements. Swan was also made a Fellow of the Royal Society.
Ultimately, Edison ended up looking like the man who invented the light bulb. This was partly because he was determined to make it available in all homes. He also benefited from the promotion Swan was forced to give him.
The truth is that Edison was one of many people who invented the light bulb as we know it today. His contributions made it better and more usable. In fact, at one point, Edison bought a patent for an incandescent bulb created by two Canadians, Henry Woodward and Matthew Evans, in 1874.
However, he was brilliant at making inventions that might not have found a lot of practical use and mainstream support. That is why his name is so strongly associated with the creation of the light bulb.
Light Bulbs Today

Today, tungsten is still the primary material used in bulb filaments due to its high melting point. In the 1920s, the frosted light bulb was invented, as well as adjusted power beam bulbs used in car headlamps. Single-use flashbulbs, used in photography, were developed in the 1930s.
However, the truth is that although Edison technically "invented" the light bulb, over 20 inventors were involved in creating the incandescent light bulb.
However, the future lies in the use of LEDs since they don't need as much energy and have a much longer life than incandescent light bulbs.
Even with modern technology, an incandescent bulb can only turn 10% of the power it draws into visible light. The rest of the energy ends up as heat.
Nonetheless, these "first" light bulbs are still being used today as they are cheap and are easy to install into existing systems. That does not mean the future of incandescent bulbs is not at risk. There is an increasing demand to replace them with more energy-efficient lighting alternatives such as LEDs.
Surprisingly, LED light was discovered by accident by Nick Holonyak as he was trying to make a laser in the 60s. Holonyak got a patent for his invention, and eventually, LEDs ended up being used in various scenarios, even as traffic lights.
However, blue LEDs, which allowed the creation of white LEDs, were discovered in the early 90s by Isamu Akasaki, Hiroshi Amano, and Shuji Nakamura. The three Japanese-American scientists won a Nobel Prize for Physics in 2014 for their invention. White LEDs are created by coating blue LEDs with phosphor.
The boundaries of lighting are still being pushed today. For instance, Phillips has come up with LED technology that can be controlled wirelessly while also changing into any number of colors from a choice of about sixteen million options.
Some lights can also be synced to music, movies, and video games. The main drawback of LEDs is the cost, but that is coming down, which might spell doom for the "first" light bulb.



